让Unity IL2CPP下的反射性能提高100倍的方法
起因
在开发Ceres(Unity蓝图插件)时,我对反射进行过一系列优化尝试。
例如对于静态函数,可以直接获取函数指针来避免反射调用。
对于实例方法,我们可以使用Open Delegate和泛型字典来缓存委托实例,用一点内存开销来提高调用性能。
然后我看到了一个有意思的仓库Meetem/ILCall,里面提到了可以使用Calli指令来直接调用IL2CPP为托管函数生成的C++函数。
这里直接非常重要,因为IL2CPP会生成一系列Invoker函数来支持反射调用。具体可以参考车神的深入浅出il2cpp:反射篇。
而ILCall仓库通过一个Hacky的方式即使用unmanaged[Cdecl]约定直接调用托管函数对应的C++函数。我们可以通过下面的方式来获取函数指针。
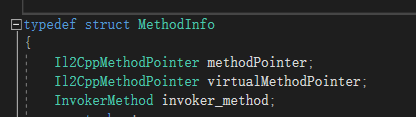
void ptr = (ulong*)MethodInfo.MethodHandle.Value
这利用了il2cpp中methodPointer对于MethodInfo的地址偏移量刚好为0的特性。
直接调用托管函数
我修改了一下代码(把结构体改成了静态类),为了方便阅读,仅保留了IL2CPP下的代码。
用dnspy反编译一部分如下:
| [MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)]
public unsafe static TReturn Generic<TReturn, TThis, T1>(TThis _this, T1 arg1, IntPtr methodPtr, void* runtimeHandleIL2CPP = null)
{
return calli(TReturn(TThis,T1,System.Void*), _this, arg1, runtimeHandleIL2CPP, methodPtr);
}
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.AggressiveInlining)]
public unsafe static TReturn Generic<TReturn, TThis, T1, T2>(TThis _this, T1 arg1, T2 arg2, IntPtr methodPtr, void* runtimeHandleIL2CPP = null)
{
return calli(TReturn(TThis,T1,T2,System.Void*), _this, arg1, arg2, runtimeHandleIL2CPP, methodPtr);
}
|
我们看看它是否有效:
C#部分:
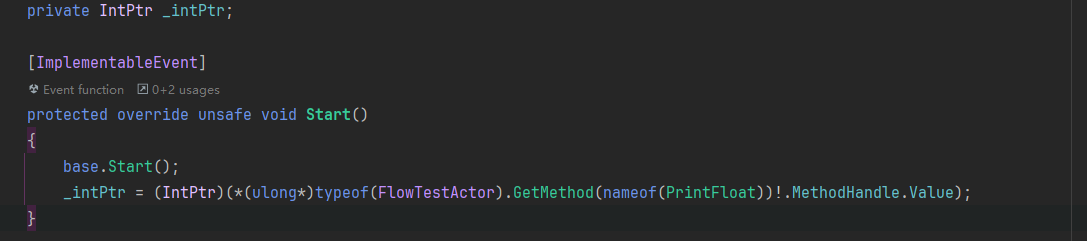
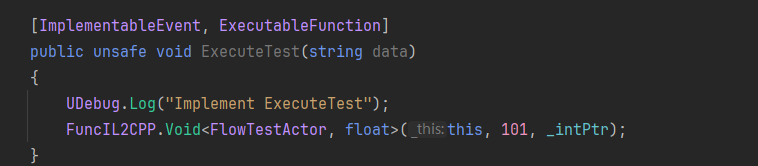
C++部分: 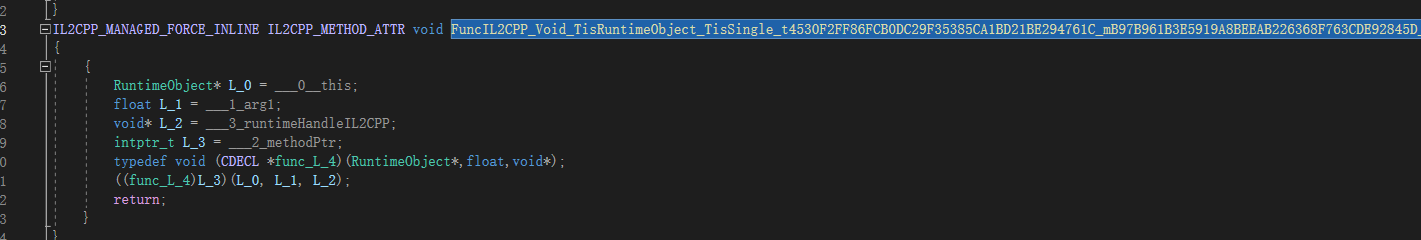
可以看到这里确实直接调用了生成的C++函数。因此在非泛型方法中使用这个Hacky方法确实是最佳实践了!
但事实上,我们可以利用C# 9提供的delegate*函数指针来实现一样的功能。
| [ImplementableEvent, ExecutableFunction]
public unsafe void ExecuteTest(string data)
{
UDebug.Log("Implement ExecuteTest");
((delegate* unmanaged[Cdecl]<FlowTestActor, float, void>)_intPtr)(this, 101);
}
|
完全泛型共享问题
然后我尝试在蓝图的泛型Invoke方法中使用这个方法,但是发现打包后抛出了异常。
| public TR Invoke<T1, TR>(TTarget target, T1 arg1)
{
if (IsStatic)
{
return ((delegate* <T1, TR>)_functionPtr)(arg1);
}
#if ENABLE_IL2CPP
return FuncIL2CPP.Generic<TR, TTarget, T1>(target, arg1, _functionPtr, null);
#else
ReallocateDelegateIfNeed<T1, TR>();
Assert.IsNotNull(_delegate);
return ((Func<TTarget, T1, TR>)_delegate).Invoke(target, arg1);
#endif
}
|
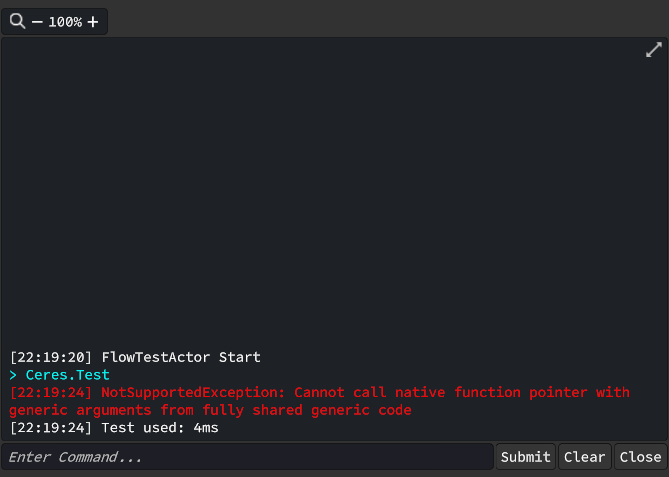
Full Generic Sharing完全泛型共享是Unity2022版本后推出的特性,以支持用户态不需要担心泛型方法被裁剪。
以下是IL2CPP翻译后的C++代码,可以看到IL2CPP不支持在泛型共享函数中调用Native指针,因为无法在编译期确定指针的类型。
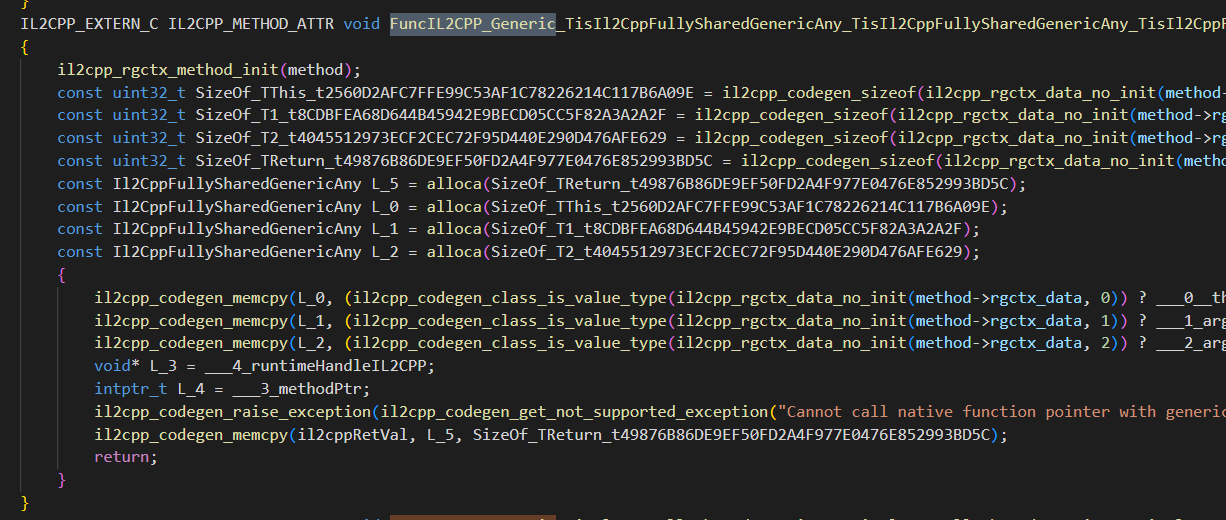
但有趣的是,IL2CPP是支持Invoke中的managed static函数指针调用的。虽然C#不支持获取和调用managed Instance函数指针,但IL实际上是支持的,可以参考Issue:Calling instance-based methods with function pointers is not supported和Discussion:Proposal: Function pointers on instance methods。
我们看下IL2CPP是如何翻译Invoke中对managed static函数指针调用的。
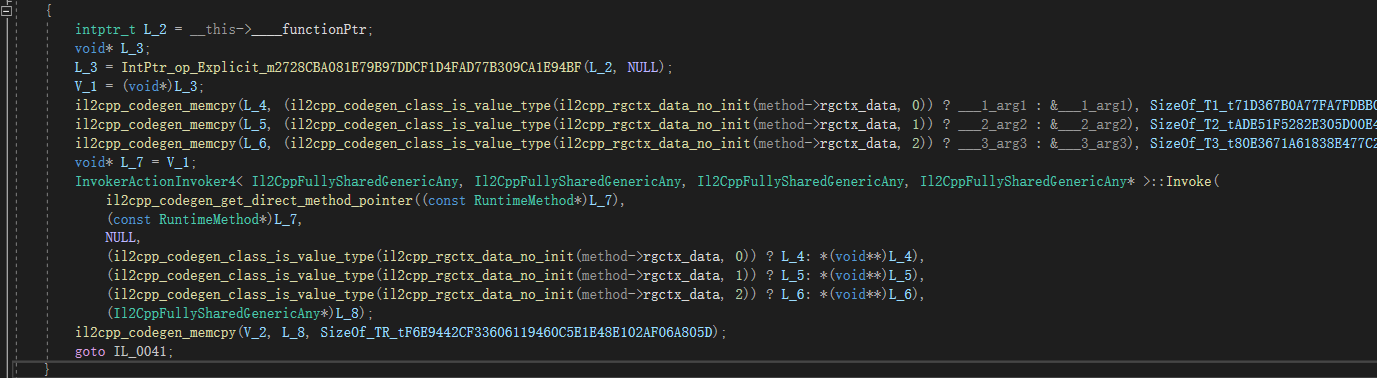
这里参考车神的文章,IL2CPP使用了一个公共的Invoker来间接调用最终的C++函数。
因此理论上IL2CPP如果能将NULL替换为我们传入的对象,就可以实现间接调用托管函数对应的C++函数,虽然不是直接调用,但相对于生成委托或直接使用反射API,开销小了很多。
间接调用托管函数
因此我修改了ILCall仓库,将其改为了IL2CPP下对Managed Instance函数的调用,因为Static函数我们可以用delegate*,不需要额外的库来做这件事了,详见AkiKurisu/IL2CPPCall。
理论上我们可以像这样使用更低开销的使用反射。
| public class MyClass
{
private int addValue = 1;
public int AddOne(int inputValue)
{
return inputValue + addValue;
}
}
int input = 5;
MyClass target = new MyClass();
var functionPtr = (void*)typeof(MyClass).GetMethod("AddOne").MethodHandle.Value;
var result = FuncIL2CPP.Generic<int, MyClass, Tint1>(target, input, functionPtr);
Debug.Log(result); // Console: 6
|
Generic方法对应的IL如下,使用了HasThis约定
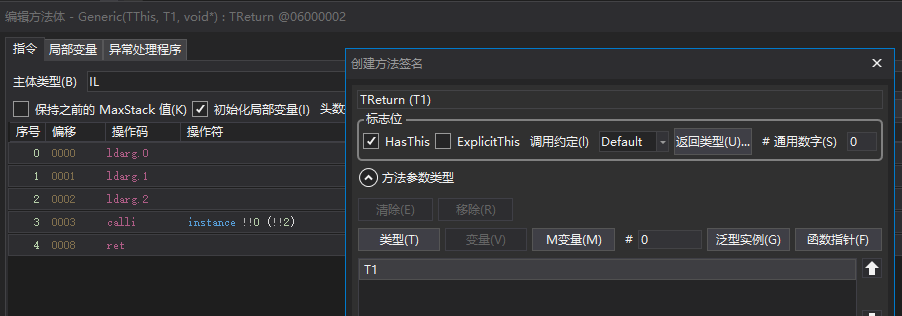
但打包后出现了错误:

因为问题出在IL2CPP内部,我们只能用dnspy来反编译Unity.IL2CPP.dll一探究竟了。
然后就发现IL2CPP在处理OpCode.Calli时未支持HasThis约定。

因此我们通过dnspy修改了IL2CPP的Unity.IL2CPP.dll,添加了对于IL2CPPCall中HasThis约定下的支持。
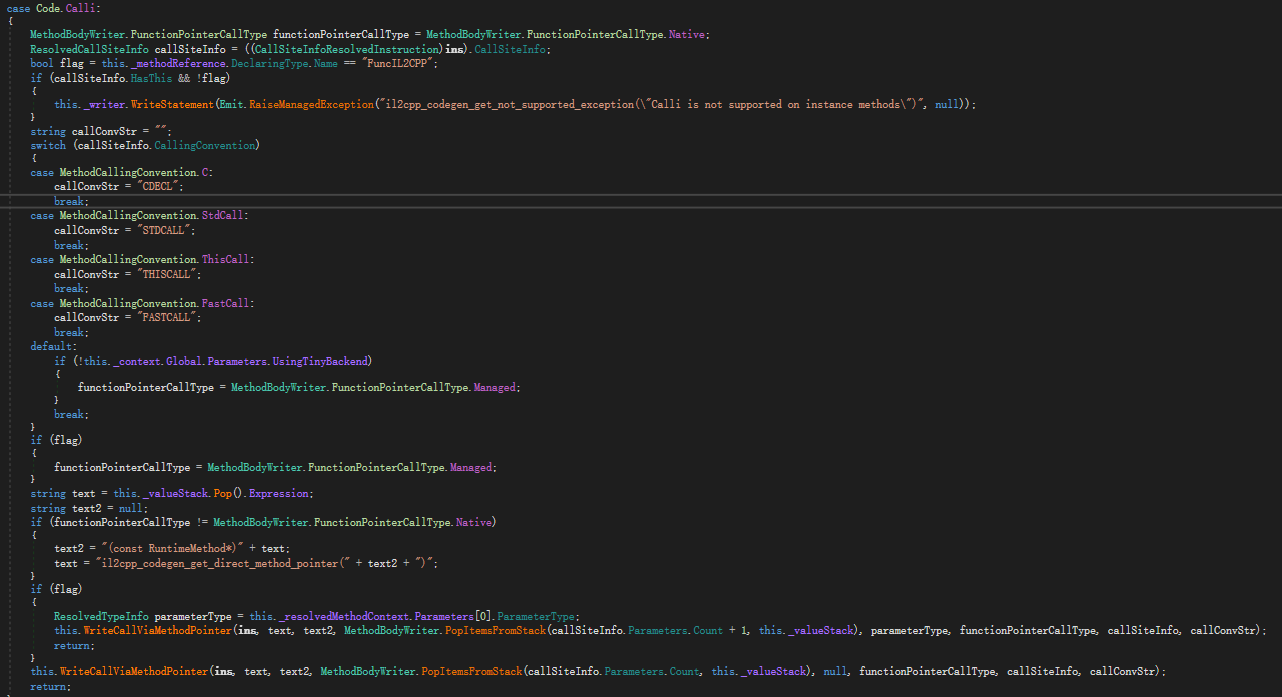
还有另一处修改,具体可参考 中的步骤。但由于IL2CPP的代码会随着Unity版本更新而更新,这个修改不保证在各个版本上统一,我这里测试的版本是Unity2022.3.13。
中的步骤。但由于IL2CPP的代码会随着Unity版本更新而更新,这个修改不保证在各个版本上统一,我这里测试的版本是Unity2022.3.13。
最后,我们打包后,发现成功了。IL2CPP为FuncIL2CPP.Generic生成了正确的C++代码。
| /* FuncIL2CPP.Generic<TR, TThisType, T1>(TThisType thisType, T1 arg1, void* methodPtr); */
IL2CPP_EXTERN_C IL2CPP_METHOD_ATTR void FuncIL2CPP_Generic_gshared (
Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny thisType,
Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny arg1,
void* methodPtr,
Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny* il2cppRetVal,
const RuntimeMethod* method
)
{
il2cpp_rgctx_method_init(method);
const uint32_t SizeOf_TThis = il2cpp_codegen_sizeof(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 0));
const uint32_t SizeOf_T1 = il2cpp_codegen_sizeof(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 1));
const uint32_t SizeOf_TReturn = il2cpp_codegen_sizeof(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 2));
const Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny L_3 = alloca(SizeOf_TReturn);
const Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny L_0 = alloca(SizeOf_TThis);
const Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny L_1 = alloca(SizeOf_T1);
{
il2cpp_codegen_memcpy(L_0, (il2cpp_codegen_class_is_value_type(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 0)) ? thisType : &thisType), SizeOf_TThis);
il2cpp_codegen_memcpy(L_1, (il2cpp_codegen_class_is_value_type(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 1)) ? arg1 : &arg1), SizeOf_T1);
void* L_2 = methodPtr;
InvokerActionInvoker2< Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny, Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny* >::Invoke(
il2cpp_codegen_get_direct_method_pointer((const RuntimeMethod*)L_2),
(const RuntimeMethod*)L_2,
(il2cpp_codegen_class_is_value_type(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 0)) ? L_0: *(void**)L_0),
(il2cpp_codegen_class_is_value_type(il2cpp_rgctx_data_no_init(method->rgctx_data, 1)) ? L_1: *(void**)L_1),
(Il2CppFullySharedGenericAny*)L_3
);
il2cpp_codegen_memcpy(il2cppRetVal, L_3, SizeOf_TReturn);
return;
}
}
|
Benchmark
最后我们对比下性能
| private IntPtr _intPtr;
private IntPtr _intPtrManaged;
private MethodInfo _methodInfo;
private Func<FlowTestActor, float, float> _delegate;
[ImplementableEvent]
protected override unsafe void Start()
{
base.Start();
_methodInfo = typeof(FlowTestActor).GetMethod(nameof(BenchmarkTestFunc));
_intPtr = (IntPtr)(*(ulong*)_methodInfo!.MethodHandle.Value);
_intPtrManaged = _methodInfo!.MethodHandle.Value;
_delegate = (Func<FlowTestActor, float, float>)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(Func<FlowTestActor, float, float>), null, _methodInfo);
}
[ImplementableEvent, ExecutableFunction]
public unsafe void ExecuteTest(string data)
{
int iterations = 1000000;
float result = 0;
var stopWatch = new Stopwatch();
stopWatch.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
result = ((delegate* unmanaged[Cdecl]<FlowTestActor, float, float>)_intPtr)(this, result);
}
stopWatch.Stop();
UDebug.Log($"Execute unmanaged[Cdecl], result {result}, used: {stopWatch.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
result = 0;
stopWatch.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
result = FuncIL2CPP.Generic<float, FlowTestActor, float>(this, result, (void *)_intPtrManaged);
}
stopWatch.Stop();
UDebug.Log($"Execute managed[HasThis], result {result}, used: {stopWatch.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
result = 0;
stopWatch.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
result = (float)_methodInfo.Invoke(this, new object[] { result });
}
stopWatch.Stop();
UDebug.Log($"Execute MethodInfo.Invoke, result {result}, used: {stopWatch.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
result = 0;
stopWatch.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
result = _delegate(this, result);
}
stopWatch.Stop();
UDebug.Log($"Execute Delegate, result {result}, used: {stopWatch.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
}
public float BenchmarkTestFunc(float data)
{
return data + 1;
}
|
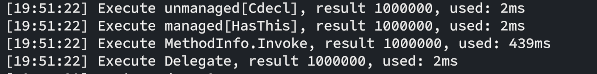
可粗略估计managed[HasThis]的性能是Invoke方式调用的百倍左右,但该用例下Delegate的性能与其基本一致,所以使用委托缓存MethodInfo是个更通用的方案。
致谢
感谢知乎/车雄生大佬的文章让我关注到反射的性能优化空间。
感谢GitHub/Meetemq的项目启发了我对反射优化的实现。
感谢Github/Stalo对我在学习IL语法和实现IL2CPPCall上极大的帮助。
中的步骤。但由于IL2CPP的代码会随着Unity版本更新而更新,这个修改不保证在各个版本上统一,我这里测试的版本是Unity2022.3.13。











